Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) are revolutionizing vehicle safety with features like adaptive cruise control, lane departure warnings, and automatic emergency braking. For these advanced systems to function accurately, ADAS calibration is essential.
Proper calibration ensures that sensors, cameras, and other related components are aligned and working as intended.
When these components are misaligned, the safety systems can become unreliable or even fail completely. You wouldn’t want your lane departure warning to give false alerts or miss a critical warning, right? Regular and precise ADAS calibration helps maintain the integrity and effectiveness of these life-saving technologies.
Definition

ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. These systems use technology to automate, adapt, and enhance vehicle systems for safety and better driving. By utilizing a network of sensors and cameras, ADAS can detect surrounding environments to provide critical information to the driver.
This includes features like forward collision warning (FCW), lane departure warning (LDW), and automatic emergency braking (AEB), which all work together to mitigate risks and prevent potential collisions.
Primary Components of ADAS
The primary components of ADAS include an array of sensors, cameras, and radar systems. Sensors are typically placed around the vehicle, such as on the windshield, bumpers, and side mirrors.
These include ultrasonic sensors for detecting objects nearby and LiDAR for measuring distances to objects. Cameras provide real-time imaging for visual systems like lane-keeping and traffic sign recognition.
Radar systems help with adaptive cruise control and blind-spot detection by scanning a broader range and detecting the velocity of objects. Together, these elements ensure the vehicle can accurately interpret its surroundings and respond appropriately.
Evolution of ADAS Technology
ADAS technology has evolved significantly from basic warning systems to more advanced semi-autonomous driving features. Initially, ADAS included simple systems like anti-lock brakes (ABS) and traction control.
Over time, innovations led to the integration of complex algorithms and machine learning, enabling functions such as adaptive cruise control and autonomous emergency braking.
Current advancements are focusing on vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication and improved sensor fusion, paving the way for higher levels of vehicle autonomy and smarter, safer driving experiences.
When is It Necessary
Calibration of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) is critical in several situations to ensure the systems function correctly. Most notably, this is essential after windshield replacement, following collision repairs, and when suspension or wheel alignment changes occur.
After Windshield Replacement
When your vehicle’s windshield is replaced, ADAS calibration becomes crucial. The sensors and cameras used by systems like lane-keeping assist and automatic high beams are often mounted on the windshield.
Replacing the windshield can misalign these sensors, leading to incorrect or malfunctioning ADAS features. Therefore, the calibration process aims to realign and adjust these sensors to the manufacturer’s settings. Accurate calibration ensures your vehicle’s safety features perform as intended, maintaining optimum safety levels.
Post-Collision Repairs
After a collision, your vehicle may require ADAS calibration to restore the proper operation of its safety systems. Accidents can disturb the alignment of sensors and cameras integrated into the vehicle’s body, bumpers, and side mirrors.
Without calibration, these disruptions can cause the ADAS to malfunction or provide inaccurate data. Technicians follow manufacturer guidelines to recalibrate after repairs, ensuring that systems such as adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking work correctly.
This step is essential for maintaining the operational integrity of your vehicle’s safety features.
Suspension or Wheel Alignment Changes
Changes to your vehicle’s suspension or wheel alignment can also necessitate ADAS calibration. Adjustments in these areas can affect the positioning of sensors and cameras that contribute to ADAS functionality.
When the alignment is not precise, the ADAS may provide incorrect feedback or fail to activate safety features as required. Calibration ensures that sensors are correctly positioned relative to the vehicle’s new alignment.
Accurate calibration is critical for the proper functionality of systems like lane departure warning and forward collision alert, thus upholding safety and performance standards.
Importance of ADAS Calibration
ADAS calibration ensures that your vehicle’s Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems operate accurately, enhancing safety features and adhering to legal standards. Proper calibration is also crucial to maintain the performance as per manufacturer specifications and preserve your vehicle’s warranty.
Safety Considerations
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) like lane-keeping assist, automatic braking, and blind-spot detection rely on precise data from sensors and cameras. Calibration aligns these components, ensuring they function correctly.
Inaccurate sensors can lead to malfunctioning safety features, such as delayed braking or incorrect lane departure warnings. This compromises your safety and that of other road users. Regular calibration prevents these issues, maintaining high safety standards.
To avoid accidents and ensure all features work as intended, ADAS calibration is essential. Accurate sensor data is fundamental for these advanced systems to provide real-time assistance and warnings, keeping you safer on the road.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Various countries have regulations requiring that ADAS-equipped vehicles undergo periodic calibration. This ensures the systems meet the safety standards prescribed by law. Ignoring these regulations can result in legal penalties or failed vehicle inspections.
Proper ADAS calibration ensures your vehicle complies with these laws, avoiding fines and other legal issues. Compliance with these regulations not only keeps your vehicle legally operable but also assures all safety features are functioning optimally.
Authorities may perform random checks or require proof of calibration, particularly after windshield replacements or collision repairs. Thus, adhering to these legal requirements through regular ADAS calibration is both a legal obligation and a safety measure.
Manufacturer Specifications and Warranty
Automobile manufacturers set specific guidelines for ADAS calibration to ensure the systems work as designed. Following these guidelines is necessary to maintain your vehicle’s warranty.
Failure to calibrate ADAS may result in the manufacturer voiding the warranty, leaving you responsible for repair costs. The precise alignment of sensors is critical for warranty claims.
Regular calibration by authorized technicians ensures your vehicle meets the manufacturer’s specifications. This not only upholds the warranty but also assures that all ADAS features operate efficiently, providing the performance and protection you expect from your vehicle.
ADAS Calibration Process
The ADAS calibration process involves a series of precise procedures to ensure that the sensors, cameras, and other components of the advanced driver assistance systems are correctly aligned and functioning. This includes both static and dynamic calibration methods, depending on the system and vehicle requirements.
Pre-Calibration Requirements
Before beginning ADAS calibration, certain preconditions must be met. Technicians need to ensure that the vehicle is on a flat surface in a well-lit area. Tire pressure should be at the manufacturer’s recommended levels, and the vehicle should have a full fuel tank.
The presence of any aftermarket modifications must be noted, as they can affect sensor alignment. Additionally, verify that all related systems are operational and there are no warning lights on the dashboard indicating underlying issues.
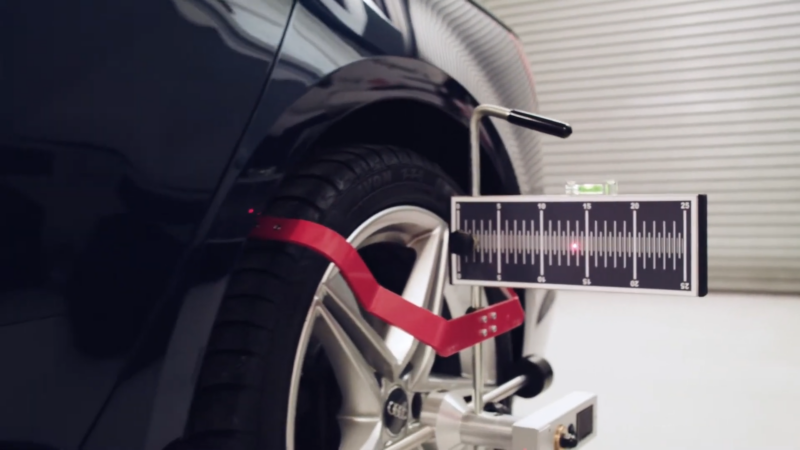
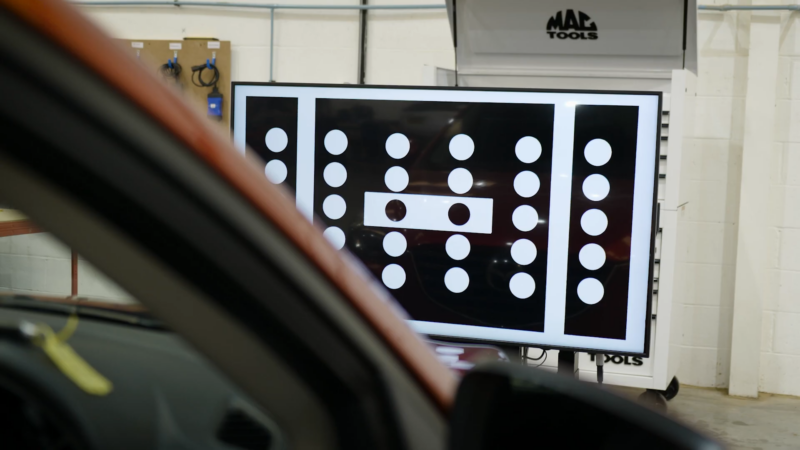
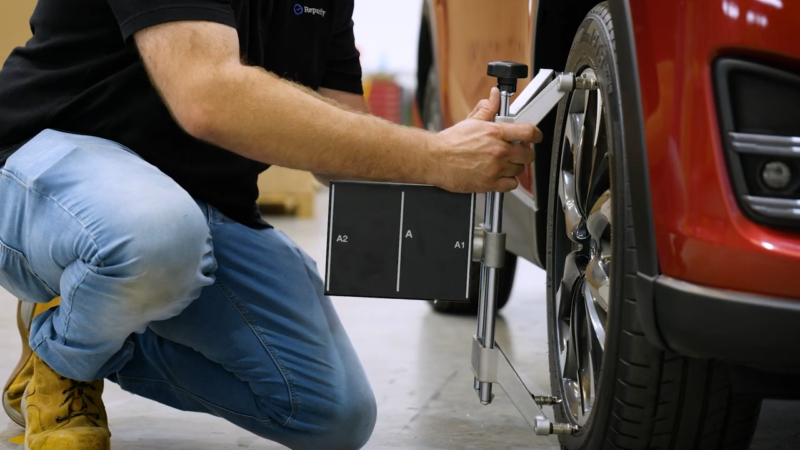
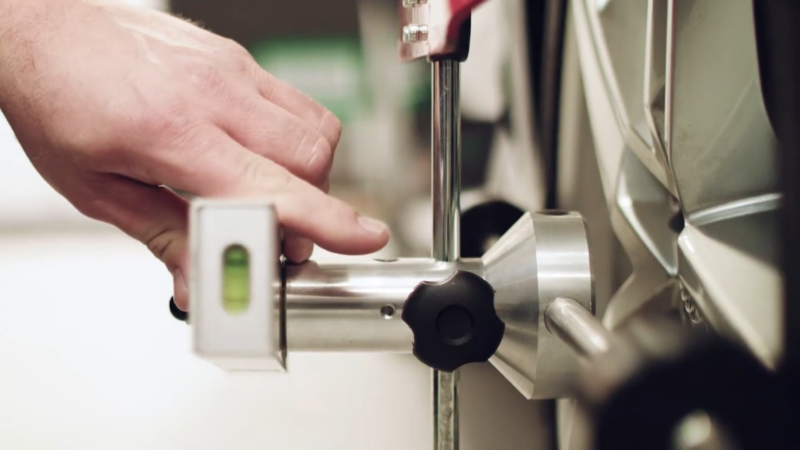
Static Calibration
Static calibration is done while the vehicle is stationary. Specialized tools and equipment are used to adjust the ADAS components. Targets are placed at specific angles and distances around the vehicle.
Cameras, sensors, and radars are aligned using these targets to ensure precise calibration. Static calibration is often performed in a controlled environment, such as a service bay, to minimize external factors like light and movement.
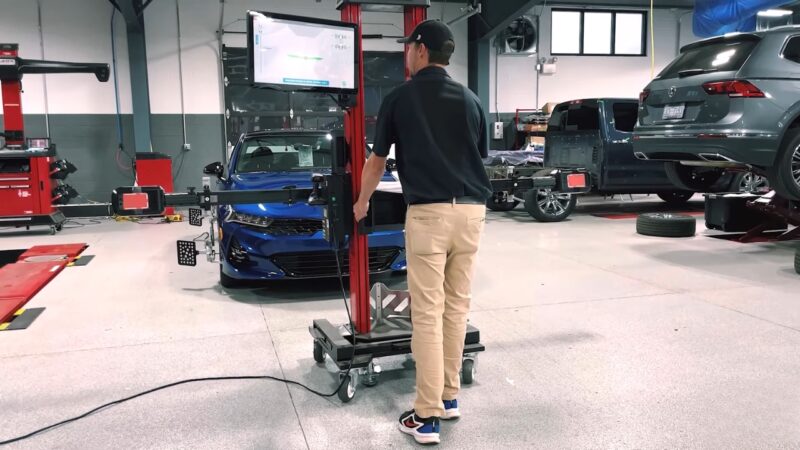
Dynamic Calibration
Dynamic calibration necessitates taking the vehicle on the road. This process involves driving at certain speeds and under specific conditions, such as clear weather and marked roadways. The vehicle’s ADAS components, such as cameras and radars, collect real-time data to self-adjust their alignment.
Technicians need to follow manufacturer guidelines meticulously to ensure accurate calibration. Factors like weather conditions and road visibility can impact the effectiveness of the dynamic calibration process. Properly calibrated systems ensure features like lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control function correctly.